Creating a solid personal finance plan is crucial for achieving your financial goals, whether it’s buying a home, retiring comfortably, or simply ensuring financial security. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential components of a robust personal finance plan, including budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. Learn how to create a personalized financial plan that aligns with your financial aspirations and empowers you to take control of your financial future.
Define What a Finance Plan Means for You
A personal finance plan is a roadmap for your financial future. It’s a detailed outline of your income, expenses, savings goals, and debt management strategies. Essentially, it’s a personalized blueprint that helps you achieve your financial objectives, whether that’s buying a house, retiring comfortably, or simply ensuring financial security.
More specifically, a finance plan provides clarity and control over your finances. It allows you to track your spending habits, identify areas where you can save money, and develop strategies to pay down debt. By setting realistic goals and establishing a budget, you gain a clear understanding of your current financial situation and can make informed decisions about your future.
Ultimately, a finance plan empowers you to take charge of your financial life. It transforms you from a passive participant in your financial journey to an active, informed decision-maker. This translates to reduced stress, increased confidence, and greater financial freedom.
Break Down Income, Expenses, and Goals
Creating a successful personal finance plan begins with a clear understanding of your financial inflows and outflows. Start by meticulously documenting all sources of income, including salary, investments, and any other regular earnings. Be as specific as possible.
Next, meticulously track your expenses. Categorize them into essential needs (housing, food, transportation), wants (entertainment, dining out), and debt payments. Utilize budgeting apps or spreadsheets to simplify this process. Identifying areas where you can reduce spending is crucial for achieving your financial goals.
Finally, define your financial goals. These could range from short-term objectives like saving for a vacation to long-term goals such as retirement planning or buying a house. Setting SMART goals – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound – will help you stay focused and motivated. Align your spending habits with your goals to ensure you’re allocating resources effectively.
Include Emergency Funds and Long-Term Goals
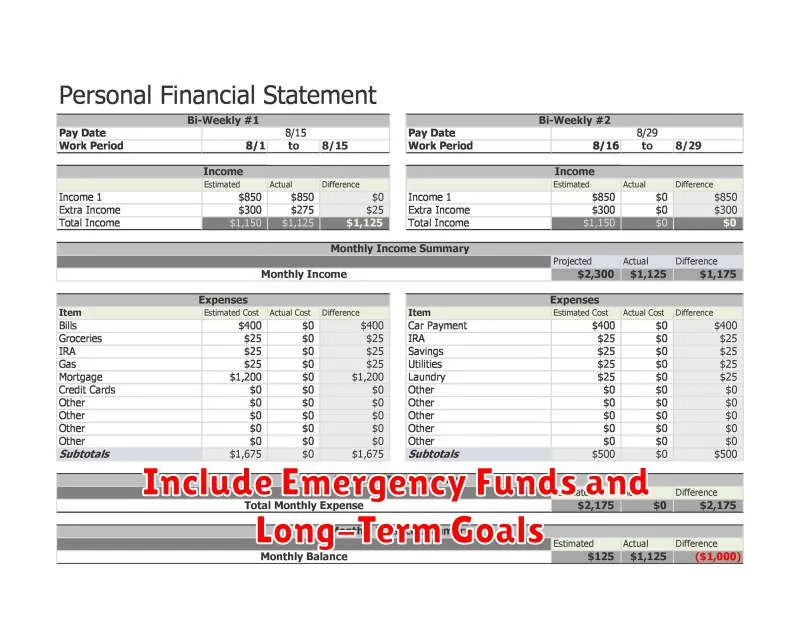
A comprehensive personal finance plan necessitates incorporating both emergency funds and long-term goals. Emergency funds act as a safety net, covering unexpected expenses like medical bills or job loss. Aim for 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in a readily accessible account.
Simultaneously, defining long-term goals, such as retirement planning, homeownership, or education funding, provides direction and motivation. These goals require strategic saving and investing over an extended period. Clearly outlining these goals, along with associated timelines and required savings, is crucial for effective financial planning.
The interplay between these two elements is essential. While emergency funds prioritize short-term financial security, long-term goals represent sustained financial well-being. Balancing these competing demands through thoughtful budgeting and investment strategies is key to achieving overall financial success.
Create Monthly Milestones and Review Them
Creating monthly milestones is crucial for tracking progress and staying on track with your personal finance plan. These milestones should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that directly contribute to your overall financial objectives.
Examples include saving a specific amount, paying down a portion of a debt, or making a significant investment. Ensure your milestones align with your larger financial goals, such as buying a house or retiring early.
Regular reviews are equally important. At the end of each month, assess your progress against your set milestones. Were you successful? If not, identify any obstacles and adjust your plan accordingly. This iterative process ensures your plan remains dynamic and adaptable to changing circumstances.
This consistent monitoring and adjustment process allows for course correction, promoting financial discipline and maximizing the chances of achieving your long-term financial aspirations.
Be Flexible but Committed to Your Plan
A successful personal finance plan requires a balance between commitment and flexibility. While it’s crucial to stick to your long-term financial goals, unexpected life events may necessitate adjustments to your plan.
Commitment involves consistently tracking your spending, saving diligently, and making regular contributions to investments. It’s about adhering to the core principles you’ve established.
However, flexibility is equally important. Life throws curveballs—job loss, medical emergencies, or unexpected expenses. Your plan should allow for adjustments to accommodate these unforeseen circumstances without derailing your overall progress. This might involve temporarily altering your savings rate or re-evaluating your spending habits.
The key is to adapt strategically. When faced with unexpected challenges, reassess your budget, prioritize essential expenses, and explore potential solutions without abandoning your long-term financial goals entirely. Regularly reviewing and updating your plan will help maintain this crucial balance.
Avoid Comparing Your Plan to Others
Creating a personal finance plan is a deeply personal journey. What works for one individual might not work for another, due to varying incomes, expenses, goals, and risk tolerances. Therefore, comparing your plan to others is generally unproductive and can even be detrimental.
Focusing on others’ financial situations can lead to feelings of inadequacy or pressure to achieve unrealistic goals. Instead of comparing, concentrate on your own unique circumstances and establish a plan that aligns with your specific needs and aspirations. Your progress should be measured against your personal milestones, not against someone else’s achievements.
Remember, the most successful financial plans are those that are consistent and tailored to the individual. Prioritize creating a plan that you understand, can realistically adhere to, and can adjust as your life circumstances evolve.
Track Progress and Update Annually
Regularly tracking your progress is crucial for the success of your personal finance plan. Annual reviews are particularly important. This allows you to assess your achievements against your goals and identify any areas needing adjustment.
During your annual review, compare your actual spending and saving against your budgeted amounts. Analyze your investment performance and any changes in your financial circumstances, such as a job change or major purchase.
Based on this analysis, make necessary adjustments to your plan. This might include modifying your budget, adjusting investment strategies, or reevaluating your financial goals. Flexibility is key; your plan should adapt to your evolving needs and circumstances.
Consistent monitoring and annual updates ensure your plan remains relevant and effective in helping you achieve your long-term financial objectives. This proactive approach prevents drifting from your financial goals and allows for course correction as needed.
